Units and Dimensions
Short Notes and Formulae
Units and Dimensions Short Notes and Formulae :
Physical quantity-A quantity that can be mea sured is called a Physical quantity.na-zn
Units-The standard quantity is known as unit, i.e., A physical quantity = nu, 6/9 100 where n = numerical value, u = units
Types of Unitstoms
(1) Fundamental Units
(2) Derived Units
(1) Fundamental Units-Those units which are independent and not related to each other.
(2) Derived Units-The units of physical quan- tities which can be expressed in terms of fundamental units are called derived units.
Example-Area, pressure, density and speed are derived quantities and their units are-Square metre, Pascal, Kilogram metre-3 and Metre second-¹ are de- rived from the fundamental units.
Definitions of some Important SI Units (1) Metre-It is the length in which 1,650,763.73
wavelength (in vacuum) of krypton-86 corresponding to the transition 2p, and 5d, lie.
(2) Kilogram-It is the mass of a litre volume of water at 4°C temperature.
(3) Second-It is duration of 9,192,631,770 periods of radiation corresponding to the transition between the two hyperfine levels of the ground state of eaesium (133) atom.
(4) Candella-It is the 1/273.16 part of the thermodynamic temperature of triple point of water. (5) Mole-It is the amount of substance of a system which contains as many elementary entituis as
there are in 1 gm of c¹2 (6) Radian-It is the plane angle between two radii of a circle which cut off on the circumference on the circle and equal in length of the radius.
(7) Steradion-The steradion is the solid angle which having its vertex in the centre of the sphere, cuts off an area of the surface of sphere equal to that of a square with sides of length equal to the radius of the sphere.

Multiplication factors of units-The multiples and sub-multiples of a unit are written by adding suitable multiplication factor as prefix to the unit. The names and symbols of various multiplication factors are shown in the table:

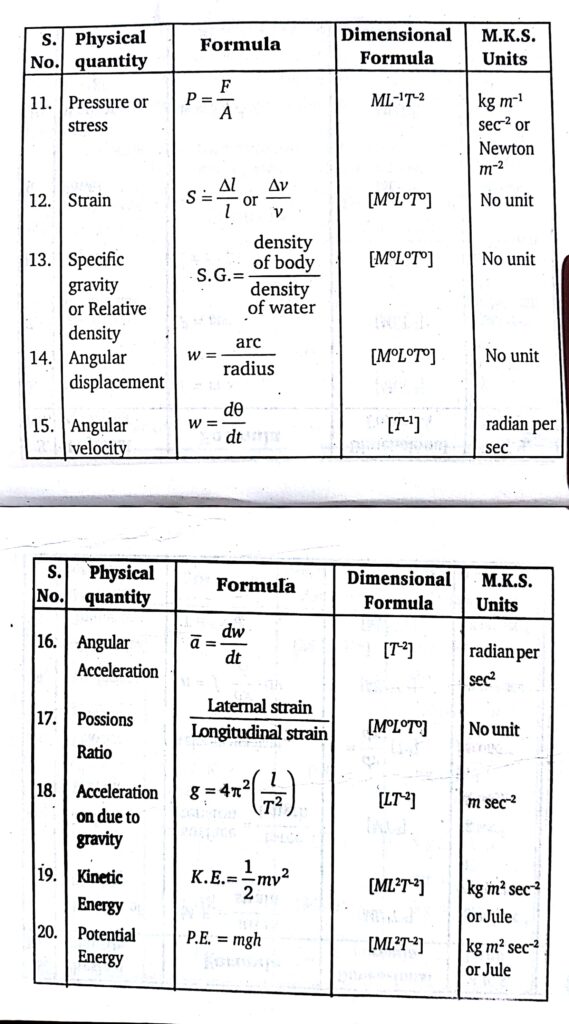
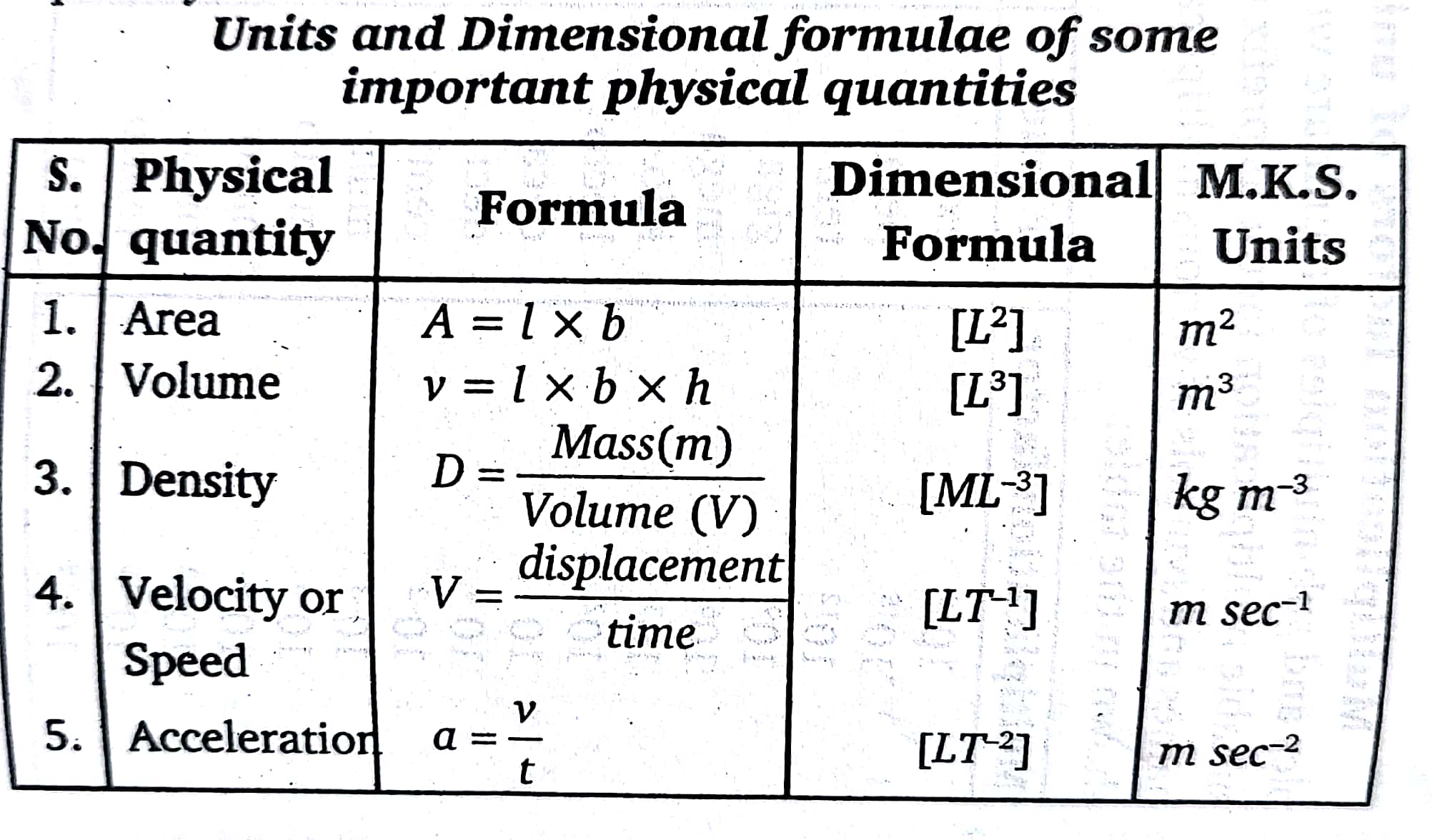
Dimensional formulae
Dimensional formulae-The expression showing the pow- ers to which the fundamental units are to be raised to obtain one unit of derived quantity is called the dimensional formula of that quantity.